Topic: Canadian Militia

Militia General Orders
His Excellency the Commander-in-Chief has made arrangements with His Excellency the Lieutenant General Commanding Her Majesty's Forces in British North America, for the establishment of a School of Military Instruction at London.
Headquarters,
Quebec, 27th April, 1865
Service Militia, Canada
General Orders, No. 1
His Excellency the Commander-in-Chief has made arrangements with His Excellency the Lieutenant General Commanding Her Majesty's Forces in British North America, for the establishment of a School of Military Instruction at London, in connection with the 1st Battalion of the 16th Regiment of Her Majesty's Forces.
This school will be opened for the reception of candidates, on Tuesday, the 16th day of May proximo, and His Excellency is pleased to order the following Rules and Regulations for the guidance of all concerned, viz.:
1. All Candidates for Commissions in the "Service" Militia, will be required before appointment, to obtain a certificate, as hereinafter mentioned, from the Commandant of one of the Schools of Military Instruction; and no person shall be appointed or promoted to the rank of Field Officer in the "Service" Militia who shall not have obtained a "First class" certificate.
2. A "First class" certificate shall be given to those candidates who shall have proved themselves, to the satisfaction of the Commandant of the School of Military Instruction, able to drill and handle a Battalion in the field, and who shall have acquired a competent acquaintance with the internal economy of a Battalion.
3. A "Second class" certificate shall be given to those candidates who shall have proved themselves able to command a Company at Battalion drill, and to drill Company at "Company drill," and who shall have acquired a competent acquaintance with the internal economy of a Company and the duties of a Company officer.
4. All candidates for admission to the Schools of Military Instruction will be required, before admission, to satisfy a Board of officers of their competence for the position of commissioned officers of the Militia.
5. No candidate shall be permitted to remain at any of the Schools of Military Instruction after he shall have obtained a second class certificate, without the special permission of the Commander in Chief.
6. No certificate of either class shall be given to any candidate who is not himself perfectly drilled as a private soldier.
7. No candidate shall be permitted to remain at any of the schools for a longer period than three calendar months from the date of his entry.
8. The traveling expenses of all candidates in coming to, and returning to their homes from the school shall be paid.
9. All candidates on obtaining a "Second Class" Certificate, shall be paid the sum of Fifty dollars, and on obtaining a "First Class" certificate, the further sum of Fifty dollars in addition.
10. All Candidates for Commissions, while attending the school, shall be considered for all purposes of drill and discipline to be attached to the Regiment which shall constitute the School of Instruction; and it shall be competent to the Commander-in-Chief, on a representation from the Commandant, to dismiss any candidate from the school, for misconduct or other sufficient cause.
11. Candidates for Commissions, while attending the school, shall not be Members of the Mess of the Regiment which constitutes the school.
No. 2.
The following officers are appointed as a Board of Examiners of candidates for admission to the School of Military Instruction at London:—
- The Commandant of the School,
- Lieut.-Colonel Shanly, Commanding Volunteers,
- Major Moffat, Brigade Major.
By Command of His Excellency the Right Honorable the Governor General and Commander-in-Chief.
Walker Powell, Lt.-Colonel, Deputy Adjutant General of Militia, Upper Canada






 Canada has six squadrons of CF-104 Starfighters with NATO, manufactured in Canada and also due to be retired in 1973. That price was about $2,000,000 a plane.
Canada has six squadrons of CF-104 Starfighters with NATO, manufactured in Canada and also due to be retired in 1973. That price was about $2,000,000 a plane.
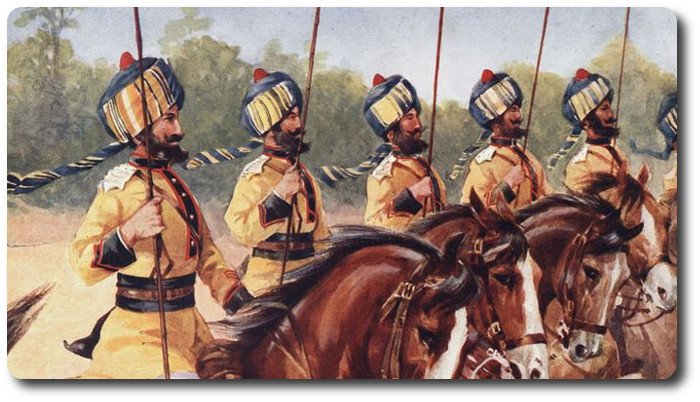






 Combat Lessons, Number 2, September 1946
Combat Lessons, Number 2, September 1946
 In Toronto there lives a retired colonel of the British army, staunch and loyal, who allowed a private soldier of good character, in the 30th Regiment, to marry his daughter. His regiment, soon after he marriage, was ordered to Montreal, and he took his wife with him, where he deserted both her and the Queen's service, and came across the lines to the protection of the stars and stripes. The colonel indignantly sent for his daughter, and she has continued to live with him, hearing occasionally from her husband, but refusing, or rather permitting her father to do it for her, to go to him as requested. Last week they were suddenly surprised by the appearance of the deserter, who entered the house without ceremony. His wife flew to him and her father at him, the latter arresting him as a deserter from Her majesty's service. In vain did the son-in-law argue and the daughter weepingly plead. With Roman firmness the British colonel insisting upon handing him over to the authorities, assuring him that thus he should treat his son or his brother, had either been a traitor. With an unyielding conviction of duty, the colonel dragged his erring relative to the barracks, and gave him up to the penalties of the law.
In Toronto there lives a retired colonel of the British army, staunch and loyal, who allowed a private soldier of good character, in the 30th Regiment, to marry his daughter. His regiment, soon after he marriage, was ordered to Montreal, and he took his wife with him, where he deserted both her and the Queen's service, and came across the lines to the protection of the stars and stripes. The colonel indignantly sent for his daughter, and she has continued to live with him, hearing occasionally from her husband, but refusing, or rather permitting her father to do it for her, to go to him as requested. Last week they were suddenly surprised by the appearance of the deserter, who entered the house without ceremony. His wife flew to him and her father at him, the latter arresting him as a deserter from Her majesty's service. In vain did the son-in-law argue and the daughter weepingly plead. With Roman firmness the British colonel insisting upon handing him over to the authorities, assuring him that thus he should treat his son or his brother, had either been a traitor. With an unyielding conviction of duty, the colonel dragged his erring relative to the barracks, and gave him up to the penalties of the law.
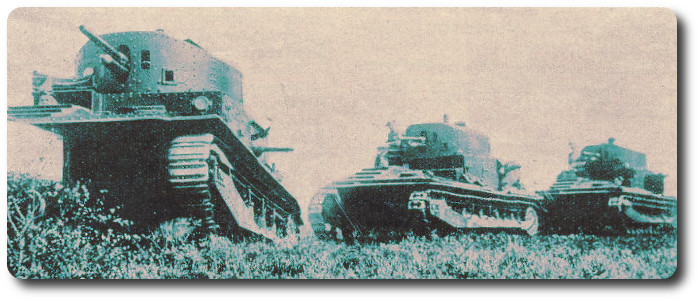

 The dispatches from General McClellan's army have several times spoken of a "regular bayonet charge." The pride of the English army has been in bayonet force.—But the dispatches state something unusual, and which must be considered complimentary to the enemy as well as to our own soldiers. We allude to the remark that the enemy were driven a mile, "during which one hundred and seventy-three rebels were killed by the bayonet alone." It is a very rare occurrence that men stand the approach of a well directed bayonet charge, and it is understood that the highest courage and daring are necessary to resists it. There are stories extant of regiments meeting bayonet to bayonet, and crossing weapons. But we do not find any authemtication of these. One favorite military anecdote relates that an English and a french regiment once met in that way and stood pressing against each other without wounding a man for a full half hour. In the Mexican war we carried several important points "with the bayonet," but this was seldom with any direct heavy charge in line.—We once asked a distinguished officer whether one of those charges was an old fashioned bayonet charge in solid rank.—He laughed and said it was very different. When the word "charge" was given the men started on a run, yelling and shouting, and throwing off all encumbrances as they ran. The very appearance of a body of furious tiger-like men, approaching at a full run, and making the air hideous with their cries, frightened the enemy from his position, and it was seldom that a man had a chance to touch another with his bayonet.
The dispatches from General McClellan's army have several times spoken of a "regular bayonet charge." The pride of the English army has been in bayonet force.—But the dispatches state something unusual, and which must be considered complimentary to the enemy as well as to our own soldiers. We allude to the remark that the enemy were driven a mile, "during which one hundred and seventy-three rebels were killed by the bayonet alone." It is a very rare occurrence that men stand the approach of a well directed bayonet charge, and it is understood that the highest courage and daring are necessary to resists it. There are stories extant of regiments meeting bayonet to bayonet, and crossing weapons. But we do not find any authemtication of these. One favorite military anecdote relates that an English and a french regiment once met in that way and stood pressing against each other without wounding a man for a full half hour. In the Mexican war we carried several important points "with the bayonet," but this was seldom with any direct heavy charge in line.—We once asked a distinguished officer whether one of those charges was an old fashioned bayonet charge in solid rank.—He laughed and said it was very different. When the word "charge" was given the men started on a run, yelling and shouting, and throwing off all encumbrances as they ran. The very appearance of a body of furious tiger-like men, approaching at a full run, and making the air hideous with their cries, frightened the enemy from his position, and it was seldom that a man had a chance to touch another with his bayonet.


 1. His Excellency the Administrator of the Government and Commander-in-Chief, having had under consideration the possibility that raids or predatory incursions on the Frontier of Canada, may be attempted during the winter, by persons ill disposed to Her Majesty's Government, to the prejudice of the Province and the annoyance and injury of Her Majesty's subjects therein;
1. His Excellency the Administrator of the Government and Commander-in-Chief, having had under consideration the possibility that raids or predatory incursions on the Frontier of Canada, may be attempted during the winter, by persons ill disposed to Her Majesty's Government, to the prejudice of the Province and the annoyance and injury of Her Majesty's subjects therein;


 Hollywood, Cal.—(AP)—If there should be another world war tomorrow the doughboys drawn from Hollywood would astonish the military experts.
Hollywood, Cal.—(AP)—If there should be another world war tomorrow the doughboys drawn from Hollywood would astonish the military experts. 
 Neither at home nor in this country is the general public so well acquainted with the marine forces as it is with the army or navy. But the British marines are indeed a credit to their country, and are generally allowed to be as fine as, of not finer, than any other branches of the service, with the exception, perhaps, of Her Majesty's Guards. Today, in Montreal, the United States marines are well represented on board the U.S. Man-of-War "Galena," and the visitor only needs to enter into conversation with them to find out what a smart and intelligent body they are. They muster but twenty-six, with one officer, Lieutenant B.R. Russell, in command, through whose courtesy the writer was enabled to find out a good deal of the interior economy, discipline, etc., of this fine corps. The "Galena" was present at Alexandria after the pillage and burning of the city, and at the bombardment; but Lieutenant Russell is the only officer on board the ship to day who was serving with her at that time. A detachment of sixty American marines was chivalrously sent by Admiral Nicholson to act with the Royal Marines of the British squadron, but their efforts were confined to putting down the plunderers and incendiaries,—after which they returned to their own ships. The "Galena" was afterwards ordered to South America.
Neither at home nor in this country is the general public so well acquainted with the marine forces as it is with the army or navy. But the British marines are indeed a credit to their country, and are generally allowed to be as fine as, of not finer, than any other branches of the service, with the exception, perhaps, of Her Majesty's Guards. Today, in Montreal, the United States marines are well represented on board the U.S. Man-of-War "Galena," and the visitor only needs to enter into conversation with them to find out what a smart and intelligent body they are. They muster but twenty-six, with one officer, Lieutenant B.R. Russell, in command, through whose courtesy the writer was enabled to find out a good deal of the interior economy, discipline, etc., of this fine corps. The "Galena" was present at Alexandria after the pillage and burning of the city, and at the bombardment; but Lieutenant Russell is the only officer on board the ship to day who was serving with her at that time. A detachment of sixty American marines was chivalrously sent by Admiral Nicholson to act with the Royal Marines of the British squadron, but their efforts were confined to putting down the plunderers and incendiaries,—after which they returned to their own ships. The "Galena" was afterwards ordered to South America.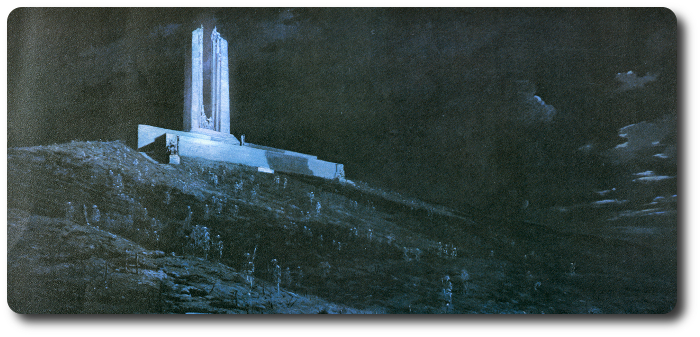
 April 9, 1917, was Easter Monday.
April 9, 1917, was Easter Monday.