Militia Is Reorganized (1936)
Topic: Canadian Militia

Non-Permanent Active Militia Is Reorganized
1936
The Evening Citizen, Ottawa; 15 December 1936
Reorganization of Canada's non-permanent active militia has been completed, and as it emerges from the crucible the new form of the Dominion's citizen soldiers is greatly dwarfed in respect of units but sturdily consistent as far as personnel are concerned.
Last night Hon. Ian Mackenzie, minister of national defence, released the whole plan involving the reorganization of the non-permanent active forces. These contemplate restriction of units but are compensated by compactness in efficiency. They also elevate the militia from the prospective to the actual.
In brief, the militia is cut down with respect to paper units. Regiments which previously existed in the militia list only on paper entirely disappear. Those which persevered strongly in the piping times of peace remain, some of them amalgamated with others, it is true, but still with enough preserved in their new name to identify them with their former lustre.
The last thing to complete the reorganization was the finding of a name for the amalgamated Royal Grenadiers of Toronto and the Toronto Regiment.
A compromise was established in re-naming the new unit "The Royal Regiment of Toronto Grenadiers." This was an 11th hour adjustment which the minister made.
System is Drastic
So far as units are concerned, the Mackenzie system is drastic, and has been in process of organization for a year. Reorganization of the non-permanent active forces was the one big problem which confronted the minister when he assumed office last year, and since then the entire department has been working to effect the adjustments now announced by Mr. Mackenzie.
The new militia is reduced from 36 cavalry regiments to 20, of which four are armored car regiments.
The 135 infantry regiments are whittled to 91. These are made up of 59 rifle battalions, 20 machine gun battalions and six tank battalions.
Artillery is increased by 52 new units. Field artillery batteries wil henceforth number 110, and increase of 41; medium batteries are increased from 25 to 31. The heavy batteries remain as at present, two, while the coast brigades are unaltered at two. However, anti-aircraft units are increased from one, plus two sections, to six, plus two sections, an increase of five.
Minister's Statement
In his statement announcing the reorganization, the minister said:
"In effecting reorganization of the non-permanent active militia the following principles were followed:
"1. Reduction of the establishment to dimensions consistent with what could be mobilized and maintained, having regard to population and financial ability.
"2. Adoption of forms of organization appropriate to modern mechanized equipment.
"3. Distribution of units (as to strength and character of service) in proportion to density of population and the dominant occupational characteristics in the various areas.
"4. Desirability of limiting to a minimum the disturbance of existing units; efficient units surplus to future requirements being permitted to convert to other and necessary types.
"5. Preservation in new and amalgamated units of the battle honors, traditions, and, part at least, of the names of former units.
"6. Full consultation with the military districts and local militia officers."
According to Districts
On the last point the minister explained headquarters had allotted to each military district the number and types of various arms and services appropriate to that district. Responsibility for detailed proposals as to the best utilizations of the approved organization within the district devolved upon the district officer commanding.
Results were attained by consultations for the district officer commanding with the officers of the units affected. Final decisions were approved by headquarters. In almost every case it was found possible to arrive at results by agreements, he added.
"In only one or two instances, where agreement could not be attained, was it considered necessary to make a decision at National Defence Headquarters," said the minister, "I am confident, however, that the decisions reached will now be loyally accepted and carried out in a spirit of good will.
Reorganization Steps
The statement contained an account of the following steps leading up to the reorganizations and an analysis of the changes effected:
Immediately after the war, establishment of the Canadian militia was set at 11 divisions and four cavalry divisions.
In 1931 an international disarmament conference was summoned to meet at Geneva on Feb. 8, 1932. Canada, faced with the necessity of filing data at this conference, notified the secretariat that in future her land forces would be limited to six divisions, one cavalry division and certain fortress and ancillary troops.
Although this decision was made by the government in 1931, no instructions to put it into effect were issued up to the time when the present minister too office on Oct, 23, 1935.
On Dec. 4, 1935, a report was laid before the minister, containing a suggested scheme for reorganization. The minister thereupon gave instructions to proceed.
A Few Units Disbanded
The reorganization is now completed. A few inactive units have been disbanded. Thirty-six cavalry regiments have been reduced to 16 cavalry regiments and four armoured car regiments.
A total of 135 infantry and machine gun battalions have been reduced to 59 rifle battalions, 26 machine gun battalions, and six tank battalion.
By conversion of cavalry and infantry units, the Royal Canadian Artillery has been increased by 41 field batteries, six medium batteries, and five anti-aircraft batteries.
Some new batteries have not yet been organized. These will be set up only as conditions in the districts require them.
Authority has been given for establishment of the Royal Canadian Engineers to 26 additional companies.
R.C.C. of Signals
On complete reorganization the Royal Canadian Corps of Signals consists of one cavalry signals, six divisional signals (two of which are distributed among several districts), two corps signals and several smaller types of units.
On reorganization each divisional army service corps is to consist of one ammunition company, one petrol company, one supply column (maintenance companies are no longer required).
In the Royal Canadian Army Medical Corps 13 surplus units, most of them inactive, have been disbanded. Officers are being reposted to remaining units.
The following other branches of the services have been reorganized. The Royal Canadian Army Ordnance Corps, the Royal Canadian Army Veterinary Corps, and the Canadian Postal Corps.

Posted by regimentalrogue
at 12:01 AM EDT







 1. The designation of the Regiment is "
1. The designation of the Regiment is "
 The London Daily News says that the unsuitability of the present regulation dress of our army for fighting and campaign purposes is held by
The London Daily News says that the unsuitability of the present regulation dress of our army for fighting and campaign purposes is held by 
 Ottawa, Aug. 23—Here and in Montreal your correspondent has watched for nigh a year the development of young men by military training. Many of them came shuffling into the ranks, somewhat stooped, pallid, enfeebles by loafing and pleasure rather than by work, which seldom harms anybody. Of late the standard of height and teeth and eyes has been wisely lowered a little, wherefore the new recruits look worse in physique than former batches. One change came over Bigs and Littles alike, swiftly rather than gradually, wonderful to behold, All were speedily improved in bearing, complexion, strength, aspect of self-respect and cheerfulness—this came of an excellent preliminary system of setting-up drill. The rapidity with which the men learned the manual of arms, and gained facility in tactical marching and evolutions, surprised one who had previously, for many years, lost few opportunities to watch Regulars and Volunteers in training. This rapidity was due, no doubt, to the fact that Canadian levies to Europe generally mustered a more intelligent sort of man, better educated on the whole, better reared, than commonly enter any regular army or militia force. True, the new levies here are animated by a spirit eager to gain fitness for active service, a spirit which gives them more alertness than men exercised as matter of mere routine. Allowing for this, the display yet vehemently reinforces a belief strong in your correspondent for forty-odd years, viz. that military training is so beneficial to Youth that it might well be required of all they suitably strong human males of any or all Nations, even if War had been put out of prospect or possibility by some all-inclusive League for Peace with general disarmament.
Ottawa, Aug. 23—Here and in Montreal your correspondent has watched for nigh a year the development of young men by military training. Many of them came shuffling into the ranks, somewhat stooped, pallid, enfeebles by loafing and pleasure rather than by work, which seldom harms anybody. Of late the standard of height and teeth and eyes has been wisely lowered a little, wherefore the new recruits look worse in physique than former batches. One change came over Bigs and Littles alike, swiftly rather than gradually, wonderful to behold, All were speedily improved in bearing, complexion, strength, aspect of self-respect and cheerfulness—this came of an excellent preliminary system of setting-up drill. The rapidity with which the men learned the manual of arms, and gained facility in tactical marching and evolutions, surprised one who had previously, for many years, lost few opportunities to watch Regulars and Volunteers in training. This rapidity was due, no doubt, to the fact that Canadian levies to Europe generally mustered a more intelligent sort of man, better educated on the whole, better reared, than commonly enter any regular army or militia force. True, the new levies here are animated by a spirit eager to gain fitness for active service, a spirit which gives them more alertness than men exercised as matter of mere routine. Allowing for this, the display yet vehemently reinforces a belief strong in your correspondent for forty-odd years, viz. that military training is so beneficial to Youth that it might well be required of all they suitably strong human males of any or all Nations, even if War had been put out of prospect or possibility by some all-inclusive League for Peace with general disarmament.



 Organization
Organization



 The
The 



 The quartermaster-sergeant marched along the communication trench and entered the firing line, says The London Chronicle.
The quartermaster-sergeant marched along the communication trench and entered the firing line, says The London Chronicle.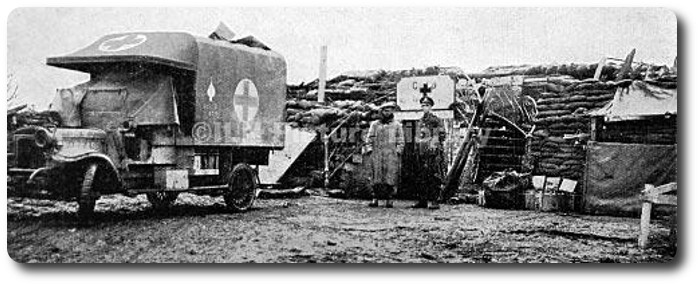
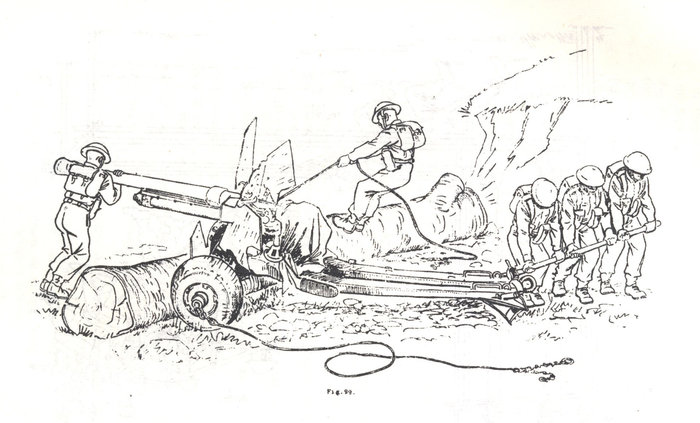
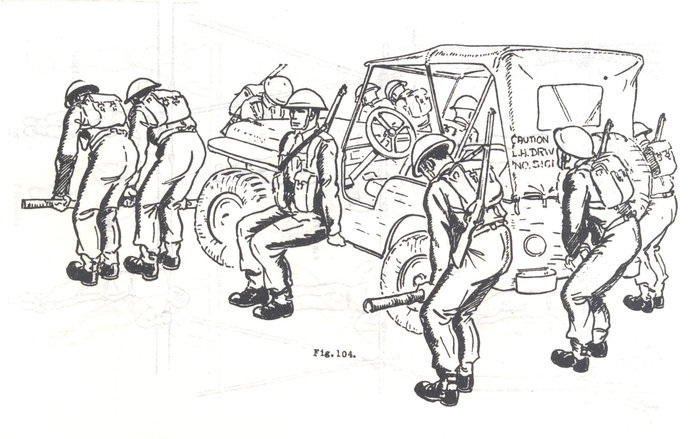
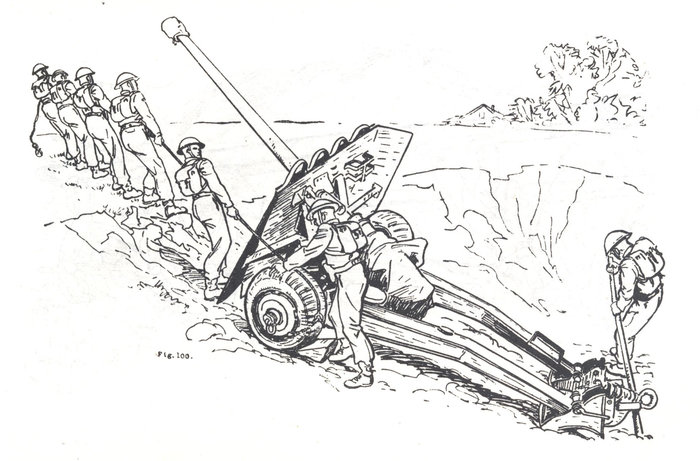
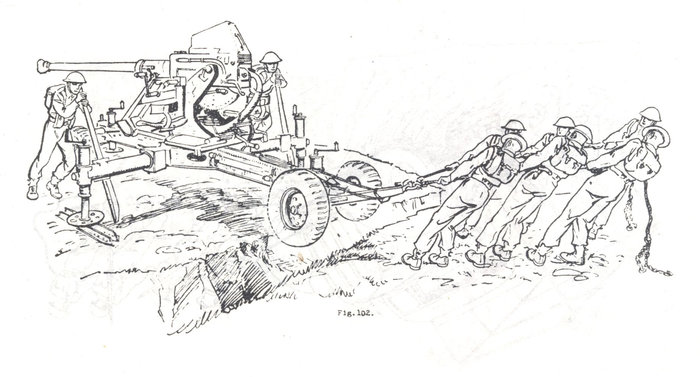
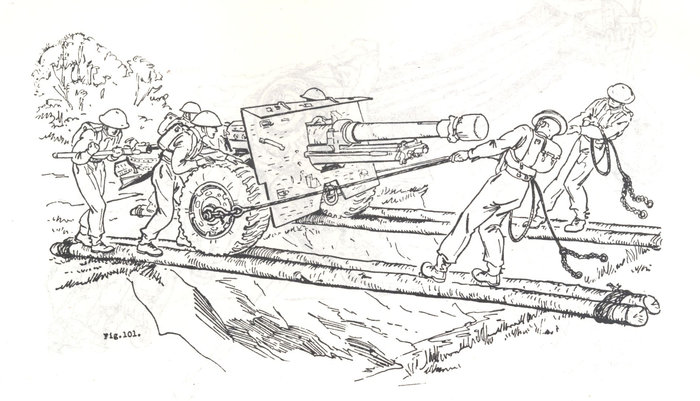
 These images, contrary to looking like methods of recovery and cross-country mobility, are taken from the publication Basic and Battle Physical Training, Part III, Syllabus of Battle Physical Training and Battle Physical Efficiency Tests (1946). The diagrams show recommended physical training exercises using available vehicles and equipment to develop both strength training and teamwork.
These images, contrary to looking like methods of recovery and cross-country mobility, are taken from the publication Basic and Battle Physical Training, Part III, Syllabus of Battle Physical Training and Battle Physical Efficiency Tests (1946). The diagrams show recommended physical training exercises using available vehicles and equipment to develop both strength training and teamwork.