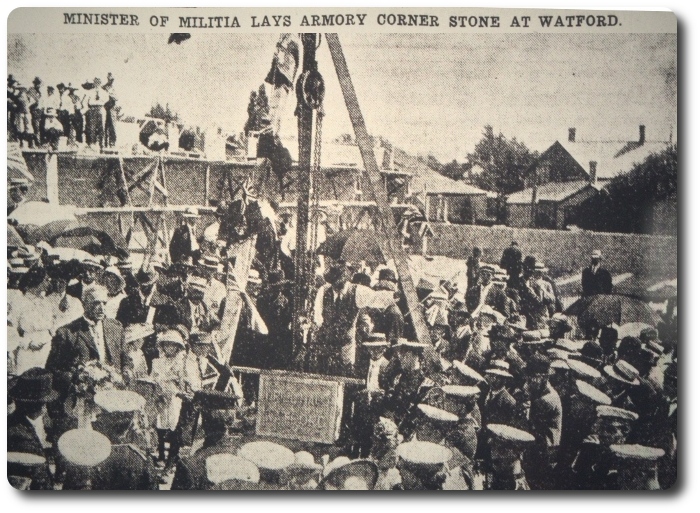
Minister Lays Corner Stone of Watford Armoury
Topic: Armouries

Minister Lays Corner Stone of Watford Armoury
Members of Parliament Are the Guests at Holiday Gathering at East Lambton
Colonel Hughes Tells of Department's Aims
Stirring Speech by Joseph Armstrong, M.P.—Reeve Stapleford Extends Official Welcome
The Free Press, London, Ont., Thursday, July 31, 1913
By Staff Reporter
Watford, July 30.—East Lambton turned out in force to-day to welcome the minister militia, Hon. Sam Hughes, on the occasion of the laying of the corner stone of the new armouries and drill hall now in course of construction here. In spite of the torrid weather, and the busy times for the farmers, over 3,000 people turned out to meet him. The greeting was most enthusiastic, and the first visit of the "war minister" was indeed an occasion long to be remembered.
Colonel Hughes arrived at noon, accompanied by Colonel Hodgins and Mr. John Farrell, of the reception committee. He was met by Reeve Stapleford and the Council together with Mr. Jos. E. Armstrong, M.P., member for East Lambton, R.J. McCormick, M.P.P., Dr. C.O. Fairbank, Petrolea, and other prominent citizens.
The Lambton Regiment was raised 14 Sep 1866 as the 27th Lambton Battalion of Infantry at Sarnia, Ontario. It was redesignated 27th Lambton Battalion of Infantry St. Clair Borderers on 1 Mar 1872, and again redesignated The Lambton Regiment 1 Dec 1920, and disbanded on conversion to artillery and engineers on 15 Dec 1936.
Escort from 27th
An escort from the Twenty-Seventh Lambton Borderers, under command of Captain R.G. Kelly, Lieutenant T.L. Swift, and lieutenant Reg. Brown and a detachment of the First Hussars, in command of Captain Abel, Lieutenant McEwen and Lieutenant Taylor, was provided. The Watford Band, reinforced by several members of the Twenty-seventh band were on hand, and as the colonel stepped from the train they struck up "O Canada." Colonel Hughes and Colonel Hodgins inspected the detachments and the parade formed.
In the first motor, driven by Mr. R. Prentis, were a number of prominent residents of the village and visitors, Colonel Hughes, Reeve Stapleford and Mr. Joseph E. Armstrong were directly in front of the band, and the parade ended at the Lyceum, where the Daughters of the Empire, with Mrs. A.G. Brown in command, served a dainty luncheon. At the head table Reeve Stapleford presided. Colonel Hughes, Mr. Armstrong, Mr. McCormick, Dr. Fairbank, Mayor Pollard, Reeve Stirrett and other prominent visitors were with him. Four charming young ladies, Misses Isabel Harris, Muriel Brown, Kate Harris and Muriel Taylor looked after their desires.
There were no speeches at this gathering. At 1.45 the parade formed and the distinguished visitors were escorted to the armouries, where the exercises were to take place.
 |  |
Cornerstone laid by Colonel Sam Hughes, Minister of Militia and Defence, on 30 July 1913. | This small plaque is inset in the Watford Drill Hall cornerstone. |
Reeve's Address
Briefly, Reeve Stapleford welcomed the visitors, and then read the following address:
Colonel Sam. Hughes, Minister of Militia:
"On behalf of the citizens of Watford we extend to you a most cordial welcome to our town, and request that you lay the corner stone of the armory and drill hall, now in course of construction, and which, when completed we feel sure will be a great convenience to our local militia and an incentive to our young men to properly fit themselves for the defence of their country, should occasion require. While 100 years have elapsed since a foreign foe has attempted to lay foot on Canadian soil, we realize that being prepared to meet an enemy id the surest guarantee of peace.
"We also wish to assure you of our appreciation of the keen interest you have always taken in the militia of our country, and trust that you may long be spared to give it your counsel.
"Signed on behalf of the municipality, Sanford Stapleford, Reeve.
Hon. Sam. Hughes was given a great reception on arising. He thanked the residents of Watford and vicinity for their cordial welcome. Little Blanche Stapleford, daughter of the reeve, presented him with a bouquet.
"You know, I have not had a bit of rest until I promised Mr. Jos. E. Armstrong, your valued member, that I would build an armory and drill hall in Watford," he declared. "I do not mind confiding to you that he led me an awful life until I did promise, and you see to-day the results of his efforts. When he invited me to come to Watford to lay the corner stone, I could not refuse."

Work of Department
Colonel Hughes gave a most interesting talk on the aims of the department. The militia was intended to inculcate into boys and young men the love of order and discipline. Lads who roamed the streets at night, untrained and undisciplined, would not become good citizens, and it was for the purpose of bringing these under the control of competent officers, to teach them the respect of authority and inculcate in them the love of country and of th empire that drill halls were being established throughout the Dominion. Military training made for good citizenship, and that made for an orderly, prosperous and happy country. Discipline, not repression, stability and usefulness, not idleness and waywardness were the aims of the department, and the results during the past two years had shown that such a policy was in the nest interests of the dominion.
The youth who went to the annual training camps was not the only care of the militia department. The cadet corps were near to his heart.
"We want to give the boys a chance," he declared. "These halls are to be their home and here they will find training in all that makes a man. We will teach then shooting, military drill, and physical training and the boys will come out better men and better citizens.
Colonel Hughes spoke of is efforts to stamp out the drink traffic at camps and in armories.
"The man who would suggest that canteens should be established in high schools or public schools would be taken to an insane asylum," he declared. "Why should drink be put in the way of boys and men in military camps. There is no difference whatever."
The military camps during the past two years has shown what had been done along these lines. The soldiers came home sober and decent, when in the past they had disgraced themselves and the uniform they wore. The ministers of the country had come to see that military camps had done much good in up-building the manhood of the country, and they were loud in their praise of the effects of the department.
Here Colonel Hughes presented Lieutenant Reg. Brown, of Watford, with the Royal Humane Society Medal, for rescuing Frank Little from drowning at Hillsboro, Lake Huron, last year.
"I am proud to present this medal, and am more proud that you wear the King's uniform," declared Colonel Hughes.
Reeve Stapleford then briefly addressed the gathering. He was pleased to welcome do large a gathering, and he was more than delighted to welcome the Minister of Militia.
"Colonel Hughes has done much for us," he declared. "We appreciate his services, and the interest our member, Mr. Joseph Armstrong, has taken in the riding, not only on this occasion, but at all times.
Mr. Armstrong
Mr. Armstrong spoke briefly. He eulogized Colonel Hughes for the great work he had accomplished in bringing the militia of the country to a higher plane. He had banished liquor from the camps, he had made the department a telling force in Canadian life. He urged a more patriotic outlook on the future of Canada. It was time that this country came to the aid of the motherland, by gifts of ships and inculcate here a more sympathetic love for the homeland.
"I say shame on the man who says that Great Britain has done nothing for us," he declared, "We owe so much to the empire, and let is stand by her loyally and manfully."
Dr. C.O. Fairbank, Mayor Pollard, and Reeve Sterrett, of Petrolea, spoke briefly as did Mr. John Farrell.
"Colonel Hughes is on the right track," said Mr. R.J. McCormick, M.P.P. "If he will keep liquor away from the camps, he will do a great deal of good, not only to the boys, but to the country."
Colonel Hodgins spoke on the work of the militia from a piratical standpoint, and urged upon the citizens to stand loyally behind the officers, in order to make the various companies strong and useful.
The distinguished visitors were escorted to the G.T.R. train by the band and guard of honor.
Much credit is due Reeve Stapleford, and the Councillors W. Doan, Jacob Fowler, John McKercher, and N. Hawn, and Messrs, R.H. Stapleford, Thomas Harris, E.D. Smith, Chester Howden, E.A. Brown, T.B. Taylor, Colonel Kenward, R. Newell, and other citizens for the successful entertainment. Captain R.G. Kelly and Lieutenant Swift were untiring in their efforts to make the affair a success, and particularly for the fine showing made by the guard of honor. The ladies were also worthy of praise.
Fowler.

Posted by regimentalrogue
at 12:01 AM EDT






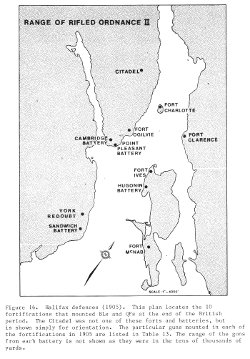
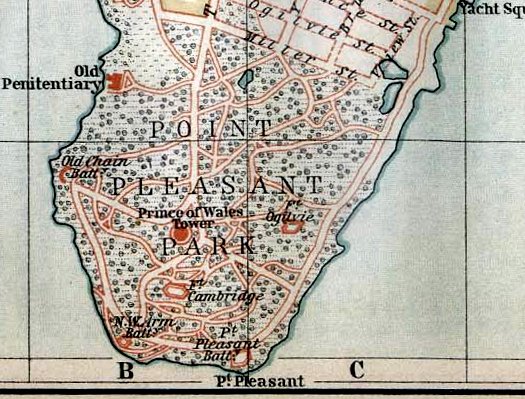 And there are more fortifications than the casual tourist can see from the harbor. I had been in Halifax for a day and was driving through
And there are more fortifications than the casual tourist can see from the harbor. I had been in Halifax for a day and was driving through 






























 Loyalty
Loyalty
 Over the past few years, my wife and I have fallen into the habit of wandering through cemeteries when we find the opportunity. She looks for those gravestones that hint at family stories of sadness or celebrations of life, while I am invariably attracted to the "soldier's stones." These soldier's stones, the
Over the past few years, my wife and I have fallen into the habit of wandering through cemeteries when we find the opportunity. She looks for those gravestones that hint at family stories of sadness or celebrations of life, while I am invariably attracted to the "soldier's stones." These soldier's stones, the 






















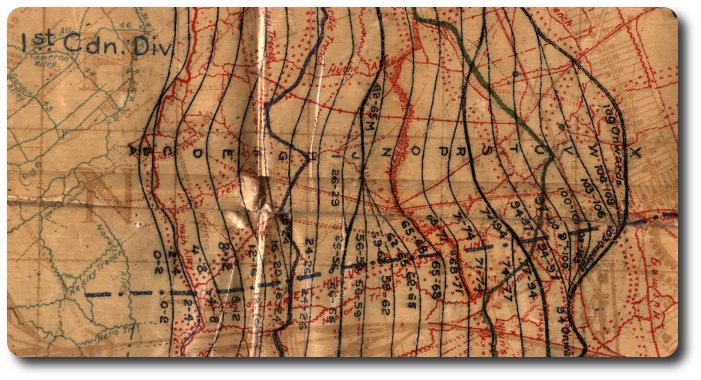






















 2. Fighting Order. — It is impossible to lay down definitely the equipment rto be carried in an attack. It must depend upon the distance of the objectives, the condition of the ground and other circumstances. Weight must always be the guiding factor in arriving at a decision in the matter of equipment. The following is suggested as a normal fighting order for all ranks of infantry, machine guns, light mortar and engineer units:—
2. Fighting Order. — It is impossible to lay down definitely the equipment rto be carried in an attack. It must depend upon the distance of the objectives, the condition of the ground and other circumstances. Weight must always be the guiding factor in arriving at a decision in the matter of equipment. The following is suggested as a normal fighting order for all ranks of infantry, machine guns, light mortar and engineer units:—






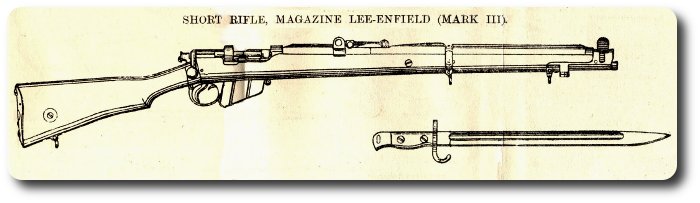
 The
The