Trench Warfare; Bombs and Grenades
Topic: CEF
Excerpted from "Trench Warfare; A Manual for Officers and Men," by J.S. Smith, Second Lieutenant with the British Expeditionary Force, E.P. Dutton & Co., 1917.
BOMBS
There are three kinds of bombs: (1) percussion; (2) ignition; and (3) mechanical. It is not possible to describe every bomb in use under these three headings, but the most typical are selected for description, although it does not follow that they are all in use at the present time, but will give a fairly good idea of what is required.
PERCUSSION BOMBS
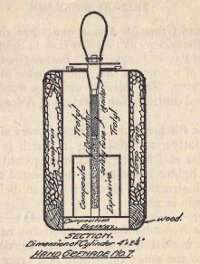
- Hand Grenade No. 1.
- Hand Grenade No. 2, formerly known as Mexican Hand Grenade.
- Rifle grenade No. 3, formerly known as Hale's Rifle Grenade.
Hand Grenade No. 1 consists of a brass case screwed on to a block of wood, to which is fixed a small cane handle about half way up the case. Outside it is a cast iron ring serrated into 16 parts. The upper end is covered by a moveable cap with a striker pin in the center. On the cap are the words "Remove," "Travel," and "Fire" in duplicate. These are marked in red and can be made to correspond with red pointers painted on case. To prepare a bomb, turn cap so that pointer is at "Remove," take off cap, insert detonator in hole and turn it to the left until the spring on the flange is released and goes into position under the pin; replace cap and turn to "Travel," which is a safety position. When the bomb is to be thrown, turn cap to "Fire" and then remove safety pin. This bomb explodes on impact, and to insure its falling on the head, streamers are attached. Care should be taken that streamers do not get entangled. The bomb must be thrown well into the air.
Hand Grenade No. 2 is similar to the above, except that a special detonator is screwed in from the head, and that the striker pin, in this case, is at the bottom. The detonator having been inserted in the bomb is ready for throwing a soon as the safety pin has been drawn.
Rifle Grenade No. 3, more commonly known as Bale's Rifle Grenade, consists of a serrated steel case filled with T.N.T. and a composite explosive. At the bottom of the case is a brass ring fitted with wind vanes, which keeps in place two small steel retaining plugs, securing the striker. In order to prepare this grenade for firing, the steel rod. attached must be put down the bore of the rifle. The safety pin is then withdrawn, the collar pulled down and the wind vane given a slight turn. The rifle is then loaded with a special cartridge containing 43 strands of cordite. When charging the rifle the bolt must be well pushed home. When the rifle is fired, the explosion of the cartridge speeds the grenade on its way and the air passing through wind vanes causes the ring mentioned above to unscrew, and the two retaining plugs to fall out. The striker is now free, and when the grenade reaches its destination and comes in contact with the ground the shock compresses the creep spring and the needle of the striker is forced into the detonator, exploding the grenade.
Special screw-in detonators are supplied with this grenade, as well as in Grenade No. 2, and care should be taken not to mix the two detonators, as the Rifle Grenade Detonator is slightly longer, and if fixed in the wrong greBnade will cause premature explosion and much sadness. These grenades have an accurate range of from 250 to 350 yards.
IGNITION BOMBS
The following bombs come under this heading:
- Hand Grenade No. 6. Grenade light friction pattern.
- Hand Grenade No. 7 Grenade heavy friction pattern.
- Hand Grenade No. 8 Formerly known as double-cylinder light pattern.
- Hand Grenade No. 9. Formerly known as double-cylinder heavy pattern.
- Battye Hand Grenade.
- Pitcher Hand Grenade.
- Oval Hand Grenade.
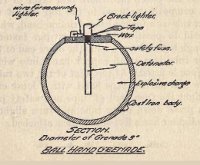
- Ball Hand Grenade.
Hand Grenades Nos. 6 and 7 consist of metal cases filled with T.N.T. and a composite explosive and are exactly alike, except that No. 7 contains shrapnel bullets or scrap iron, while No. 6 contains only explosive. At the top of each case is a place to fix the friction igniter, which is supplied separately. When these bombs are to be used, detonator fuse and igniter are put in and firmly fixed. Before throwing the becket on, head of igniter should be pulled smartly off.
Hand Grenades Nos. 8 and 9 are similar to the above, except that the fuse is lighted by a Nobel Patent Lighter. The Battye Grenade consists of a grooved cast iron cylinder filled with explosive. The top is closed by a wooden plug pierced centrally for insertion of detonator and fire.
The Pitcher Hand Grenade is very similar to the Battye, only different in that it is slightly heavier and having a different patent lighter. This lighter is somewhat complicated and special instructions should be given before the grenade is used.
The Nobel lighter consists of two cardboard tubes, one fitting over the other. Inside the top end of the outer tube there is a layer of friction composition; fixed to the top end of the inner tube is a forked brass friction head, which is held in position by a safety pin fastened through both tubes. Inside the other end of the inner tube is a small copper band, into which the fuse is fitted. At the joint of the two tubes there is a narrow tape band with a loose end. To light the fuse, pull off tape and safety pin, then press down outer tube and turn slightly. This lighter has a five-second fuse attached.
The Oval Hand Grenade is an egg-shaped cast iron receptacle filled with ammonal. One egg has a steel plug and the other a flanged brass plug bored centrally, to which a hollow copper tube is fixed to take the detonator. This grenade is set off by a Brock fuse and lighter.
The Ball Hand Grenade consists of a cast iron sphere, 3 inches in diameter, filled with ammonal and closed by a screwed steel plug which has attached to it a covered tube to take detonator in the center of grenade. It is also lighted by a Brock lighter.
JAM-POT BOMBS. In the early stages of the war it was found necessary to make bombs on the spot. The material used was generally a jam tin filled with shrapnel bullets, scrap iron, powdered glass and grass, etc. This was exploded by 2 one-ounce primers, two ounces gelignite, blastene or ammonal, and detonated by a No. 6 or 7 detonator, to which was attached a five-second fuse. The time could be regulated by length of fuse.
The Brock lighter consists of a match-head and fuse combined. The head consists of a small cardboard cup filled with friction composition and covered with waterproof paper. With this type of lighter an armlet covered with match composition is worn by the bomber on the left forearm. To ignite fuse, first pull off waterproof paper and then strike head against armlet. Time of fuse 5 seconds.
MECHANICAL BOMBS
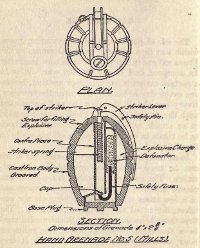
Hand Grenade No. 5, known as Mills' Hand Grenade. Mills' Hand Grenade No. 5 weighs about one and one-half pounds and is in constant and steady use at the front, being the best known of all grenades. It consists of an oval cast iron case, containing explosives and serrated to provide numerous missiles on detonation. In the center is a spring striking pin, kept back by a lever or handle, which, in its turn, is held in position by a safety pin.
Detonators and percussion caps connected by a short length of fuse are supplied with these bombs. When the bomb is to be used the bottom is unscrewed and the combined detonator and percussion cap is inserted in the space provided for it, the percussion cap being placed in the boring under the striking pin. When this is done the bottom is screwed on again as tightly as possible, using the special spanner provided for this in each box. Before throwing, the safety pin is removed and the bomb held with the lever in the palm of the hand. When the bomb is actually thrown the lever or handle is released; this releases the spring, which forces striker down on to the percussion cap, ignites fuse, sets off detonator and explodes bomb.
See also the Great War Forum, thread with images: Mills Bomb
Joseph Shuter Smith
Joseph Shuter Smith was an American author born in Philadelphia in 1893. He spent his childhood in Alaska during the Gold Rush and spent his years before the Great War as a lumberjack, miner, surveyor and cowboy. In 1914, continuing his adventurous streak, he went to Canada and enlisted in the Canadian Expeditionary Force, declaring his birthplace to be Port Hope, Ontario (with next of kin in Oakland, California). Smith enlisted with the 29th Canadian Infantry Battalion at Vancouver. He served in France and Belgium as a soldier in the CEF and, after being commissioned in August, 1916, as an officer of the British Army with The Royal Scots (Lothian Regiment). He resigned his Imperial commission after a year to return to the US and enlist in the American Army. Joseph Smith also wrote the memoir: Over There and Back in Three Uniforms; Being the Experiences of an American Boy in the Canadian, British and American Armies at the Front and through No Man's Land.

Posted by regimentalrogue
at 12:01 AM EDT
 S.7. – Training of the Men
S.7. – Training of the Men











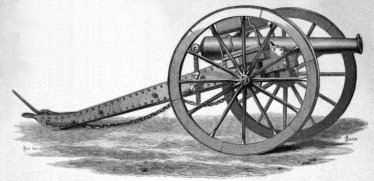 To be competed for on parade during annual drill by the four sub-divisions of the Battery. the prizes to be awarded to the Batteries performing the conditions in the shoertest average time.
To be competed for on parade during annual drill by the four sub-divisions of the Battery. the prizes to be awarded to the Batteries performing the conditions in the shoertest average time. 

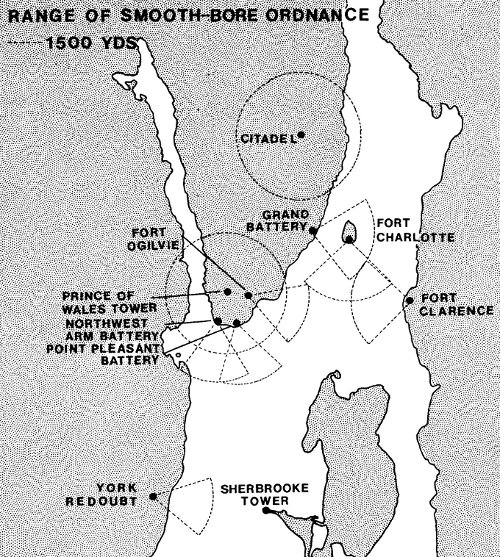 The likeliness of congestion in the main harbour from burning ships and damaged docksides, the steep approach through the town and being under the guns of the fortress make that approach an undesirable on for an attacker. The alternatives, therefore, would be landing on
The likeliness of congestion in the main harbour from burning ships and damaged docksides, the steep approach through the town and being under the guns of the fortress make that approach an undesirable on for an attacker. The alternatives, therefore, would be landing on 

 Military Customs
Military Customs
 The Royal Fusiliers (City of London Regiment)
The Royal Fusiliers (City of London Regiment) Excerpts from the pages of On the Psychology of Military Incompetence, by Norman F. Dixon (1976).
Excerpts from the pages of On the Psychology of Military Incompetence, by Norman F. Dixon (1976). General:
General:



 The uninitiated might ask: "How many possibilities could there be for medal collecting themes?"
The uninitiated might ask: "How many possibilities could there be for medal collecting themes?" And here's where it gets complicated. Any collector might combine any variety of "simple" themes, perhaps defining their interests as:
And here's where it gets complicated. Any collector might combine any variety of "simple" themes, perhaps defining their interests as:

 Issued under the authority of
Issued under the authority of 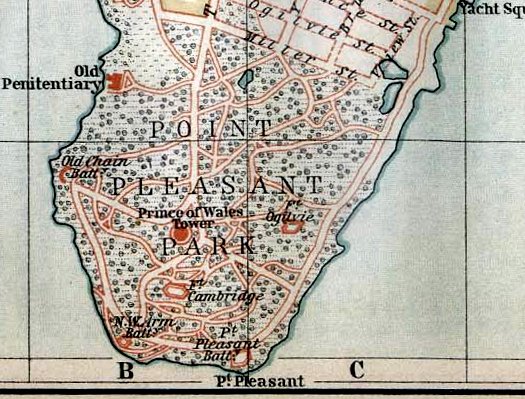
 Many members of
Many members of 

 There always seems to be someone ready to denigrate the collector of military medals. "Profiting off their honour," they'll say, or "dishonouring the heroes." Sometimes, it's snide remarks inferring that the medals held by collectors must have been received via nefarious means, either stolen from families or swindled from poor widows. Collectors have even been called the "
There always seems to be someone ready to denigrate the collector of military medals. "Profiting off their honour," they'll say, or "dishonouring the heroes." Sometimes, it's snide remarks inferring that the medals held by collectors must have been received via nefarious means, either stolen from families or swindled from poor widows. Collectors have even been called the " "Ban the sale of medals!" is an occasionally heard rally cry, one sometimes taken up by politicians seeking favour with constituents who might support such a measure. But this argument also is seldom fully developed; emotional cries for change seldom are. Should medals cease to be personal property, returned to the Crown on the death of the recipient? Would that not also prevent them passing to direct descendants? Or should families be required to register and retain them, releasing them only back to the Government to be held in an approved repository like a museum? How would we track such things, with a medal registry? What would we do with current collectors, seize their collections or grandfather them without allowance to resell ever?
"Ban the sale of medals!" is an occasionally heard rally cry, one sometimes taken up by politicians seeking favour with constituents who might support such a measure. But this argument also is seldom fully developed; emotional cries for change seldom are. Should medals cease to be personal property, returned to the Crown on the death of the recipient? Would that not also prevent them passing to direct descendants? Or should families be required to register and retain them, releasing them only back to the Government to be held in an approved repository like a museum? How would we track such things, with a medal registry? What would we do with current collectors, seize their collections or grandfather them without allowance to resell ever?  While some collectors may hoard and keep secret their collections and the research they have gathered, often it is because they have found that tactic protects them from the very accusations identified above. But in this increasingly connected world, more collectors are speaking out and sharing the knowledge they have about individual recipients, about the units and battles they have researched, and about the techniques they use both to find information and to preserve and display their collections.
While some collectors may hoard and keep secret their collections and the research they have gathered, often it is because they have found that tactic protects them from the very accusations identified above. But in this increasingly connected world, more collectors are speaking out and sharing the knowledge they have about individual recipients, about the units and battles they have researched, and about the techniques they use both to find information and to preserve and display their collections.  Following the First World War, many tried their hands at literary pursuits, from the well-known war poets to others who wrote the stories of their service. Following these better known examples, there were also some who tried to fill in every imaginable niche, penning works of interest for those with a lingering interest in understanding the late war and its soldiers. One of these was John Hay, with his volume "Humour in the Army" (pub. by Hazell, Warson & Viney, Ltd., 1931).
Following the First World War, many tried their hands at literary pursuits, from the well-known war poets to others who wrote the stories of their service. Following these better known examples, there were also some who tried to fill in every imaginable niche, penning works of interest for those with a lingering interest in understanding the late war and its soldiers. One of these was John Hay, with his volume "Humour in the Army" (pub. by Hazell, Warson & Viney, Ltd., 1931).
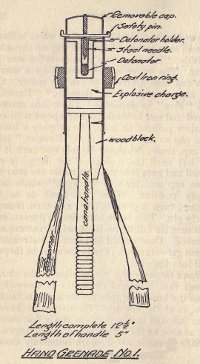
 During the
During the