Topic: Wolseley Barracks

Members of Parliament who are quoted below are:
- The Hon. Joseph Philippe René Adolphe Caron, P.C.; Conservative Member for Quebec County, Quebec (Appointment at the time of this session: Minister of Militia and Defence)
- The Hon. Sir Hector-Louis Langevin, P.C., Q.C., C.B.; Conservative Member for Three Rivers, Quebec. (Appointment at the time of this session: Minister of Public Works 1879 – 1891)
- The Right Hon. Sir William Mulock, P.C.; Liberal Member for York North, Ontario
- The Hon. Edward Blake, P.C., Q.C.; Liberal Member for Durham West, Ontario
House of Commons of the Dominion of Canada
Fourth Session – Fifth Parliament
2 June 1886
London Infantry School – $30,000
Mr. Blake – Will the hon. gentleman explain the vote of $30,000 for the London Infantry School?
Sir Hector Langevin – It is to enable the chief architect to carry on the work of the proposed new barracks. The cost of the barrack building, including furnishing, heating, etc., is estimated at $75,000; then there is $3,600 for the architect and $2,000 for the clerk of works, the total estimated cost being $81,000.
Mr. Blake – Has the hon. gentleman received any information as to difficulties with the drainage of the site of the school.
Sir Hector Langevin – I have not.
Mr. Blake – It has been stated in the papers that there are serious difficulties, and that pile driving will have to be resorted to in order to overcome them.
Mr. Carling – The architect was in the city yesterday, and he says that the difficulty can be overcome by the construction of a drain.
Mr. Blake – I suppose this is the property as to which the tripartite agreement was made some time ago, under which the city bought some property from the Minister of Agriculture, and the hon gentleman took that property and gave the city some other property?
Sir Adolphe Caron – Yes
Mr. Blake – Will the hon. gentleman state the nature of the arrangement?
Sir Adolphe Caron – In 1884, on the recommendation of General Middleton, it was determined to establish an Infantry School in London. The citizens of London were very adverse to the school being established on the Government Property, for reasons which they set forth. Upon that recommendation, three sites were offered, the Geary site, the Kent Site, and the Carling farm. The matter was submitted to the brigade major of the district, and he recommended the Carling farm as the most suitable. The offer made to the city was $10,000 in cash and a deed of 16 acres of land of Government property and the right to use some 90 acres adjoining for camping purposes for 20 years, for 8 acres of land now used as our military property. The proposition was approved by Order in Council; but it had to be submitted to a vote of the ratepayers of London, who rejected it. Subsequently, however, the city made a new proposition, that they would give a free deed of fifty-five acres of the Carling farm within city limits, which has been used as a military camp-ground for many years, for eight acres of the Government property referred to in the former proposition. This proposition was again referred to the brigade major, and was referred by him to Mr. George Durand, a well-known architect of London, on the 26th of April, 1885. A valuation of the two properties was sent in by him. The Government property was estimated at $141, 355 and the fifty–five acres of the Carling farm were estimated at $46,000. I was not satisfied to take this valuation; I wanted to get more than one, and the proposition was again submitted to the valuation Mr. McElheran, and auctioneer and valuator, and Mr. William M. Ward, a real estate agent, and these gentlemen reported the value of the Government property at $39,030, and the fifty-five acres of the Carling farm at $44,000. This subsequent offer of exchange was referred to the council and approved, and the exchange has been made, and the contract for the building let, and the work is now going on. I will bring down and lay on the Table all the papers.
Mr. Blake – Is Mr. Durand the architect of the building now?
Sir Hector Langevin – Yes.
Mr. Blake – It has been represented outside, from time to time, that this institution, which is to be erected in or near London, is to be analogous to the Kingston College.
Sir Adolphe Caron. – No; it is to be analogous to the School of Infantry, Toronto.
Although Mr Durand is identified above as the architect for the new Infantry School in London, the building was designed by Henry James, Chief Architect for the Militia Department. (With thanks to Dr Georgiana Stanciu, Curator of The Royal Canadian Regiment Museum, for this confirmation.)

 An essential part of the equipment and references carried by every officer of the British Army and Commonwealth forces in the early 1900s was a copy of the Field Service Pocket Book. The standard aide memoire of officers on operations anywhere in the Empire, this little volume provided all manner of information necessary for planning and conducting operations, ranging through staff duties, rates of march, engineering and logistic guidance, and details on the forces of the Empire.
An essential part of the equipment and references carried by every officer of the British Army and Commonwealth forces in the early 1900s was a copy of the Field Service Pocket Book. The standard aide memoire of officers on operations anywhere in the Empire, this little volume provided all manner of information necessary for planning and conducting operations, ranging through staff duties, rates of march, engineering and logistic guidance, and details on the forces of the Empire.


 THE ROYAL CANADIAN REGIMENT
THE ROYAL CANADIAN REGIMENT PRINCESS PATRICIA'S CANADIAN LIGHT INFANTRY.
PRINCESS PATRICIA'S CANADIAN LIGHT INFANTRY.  42ND BATTALION, (5TH ROYAL HIGHLANDERS OF CANADA).
42ND BATTALION, (5TH ROYAL HIGHLANDERS OF CANADA). 49th BATTALION (CANADIANS).
49th BATTALION (CANADIANS).

 The RCR would serve in France and Flanders from November 1915 until the end of the War and approximately 4800 Canadians would wear the Regiment's
The RCR would serve in France and Flanders from November 1915 until the end of the War and approximately 4800 Canadians would wear the Regiment's 

 On
On 


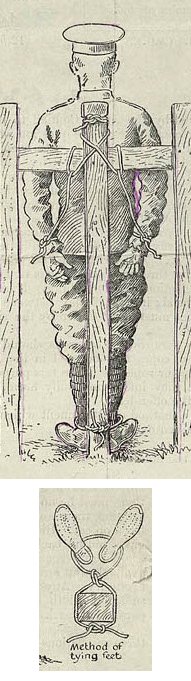 Many old soldiers like to talk about the "good old days" when, in their hazy remembrance, soldiers were more disciplined, less likely to question any aspect of military life, and worked and played harder. While the achievements of the Canadian Army in
Many old soldiers like to talk about the "good old days" when, in their hazy remembrance, soldiers were more disciplined, less likely to question any aspect of military life, and worked and played harder. While the achievements of the Canadian Army in 
 The first medal that many Canadian soldiers might have been eligible to receive for their First World War service was the
The first medal that many Canadian soldiers might have been eligible to receive for their First World War service was the 

 Instead, we find that widespread service was made of the British Amy's existing solution for clothing recuperating solders, the "hospital blues." Blue linen suits, lined in white and nattily accessorized with a bright red tie. What self-respecting soldier wouldn't find that outfit stylish and debonair for "walking out" during his convalescence, especially since they came in a range of few sizes fitting few soldiers well. Although originally cut to be buttoned to the neck, turning down the collar of the jacket added the benefit of bright white lapels to the hospital blues' appeal.
Instead, we find that widespread service was made of the British Amy's existing solution for clothing recuperating solders, the "hospital blues." Blue linen suits, lined in white and nattily accessorized with a bright red tie. What self-respecting soldier wouldn't find that outfit stylish and debonair for "walking out" during his convalescence, especially since they came in a range of few sizes fitting few soldiers well. Although originally cut to be buttoned to the neck, turning down the collar of the jacket added the benefit of bright white lapels to the hospital blues' appeal.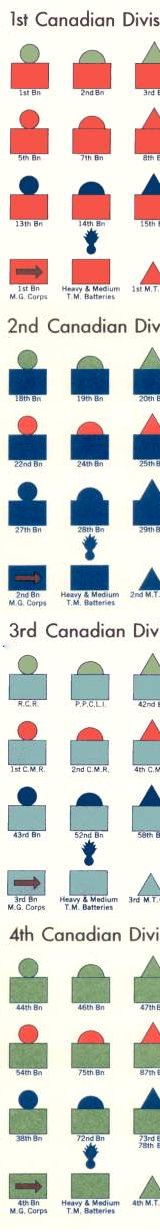 (Or: "How One Regiment Could be Fighting in Three Places at Once")
(Or: "How One Regiment Could be Fighting in Three Places at Once") The Guide: A Manual for the Canadian Militia (Infantry)
The Guide: A Manual for the Canadian Militia (Infantry)


 Equipment
Equipment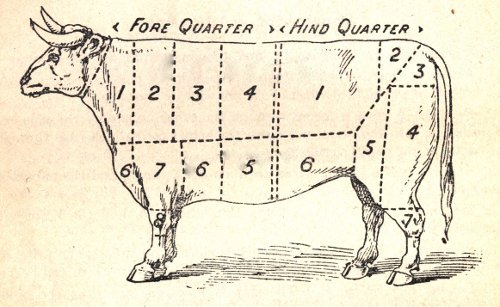


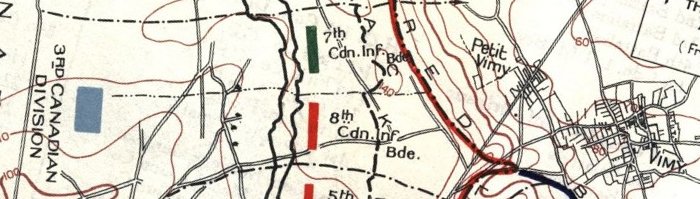
 We often hear catchphrases but we can never quite be certain where they originated. Infantry officers training in the Canadian Army have long head one which goes "Time spent on recce (i.e, reconnaissance) is never wasted" … intending to teach the new officer that even if he or she thinks they understand a situation completely, a thorough reconnaissance (time permitting) is invaluable, if for no other reason to confirm what is known. Inevitably, in training and service afterwards, reconnaissance often identified factors that were previously not known to the officer and which materially affect the plan evolving in their mind. failing to heed this adage can have serious consequences.
We often hear catchphrases but we can never quite be certain where they originated. Infantry officers training in the Canadian Army have long head one which goes "Time spent on recce (i.e, reconnaissance) is never wasted" … intending to teach the new officer that even if he or she thinks they understand a situation completely, a thorough reconnaissance (time permitting) is invaluable, if for no other reason to confirm what is known. Inevitably, in training and service afterwards, reconnaissance often identified factors that were previously not known to the officer and which materially affect the plan evolving in their mind. failing to heed this adage can have serious consequences.