Canadian Infantry Organization (1916)
Topic: Canadian Militia

Canadian Infantry Organization (1916)
The infantry is the main arm of every Army.
The Organization, Administration and Equipment of His Majesty's Land Forces in Peace and War, First Edition, by Lieut.-Colonel William R. Lang, m.s.c, 1916
Infantry Units in Canada
The infantry is the main arm of every Army. The following are the Infantry units in Canada:—
Permanent Force:—
The Royal Canadian Regiment. The R.C.R. dates its organization as a Regiment from Dec. 21st, 1883, and has its Regimental Headquarters at Halifax, Nova Scotia. It maintains detachments or companies at various stations, namely at London, Toronto, Fredericton, N,B., Halifax, N.S., Quebec, P.Q., Esquimalt, B.C., where in peace time Schools of Instruction are held for Officers and N.C.O.'s of the non-permanent Militia. The establishment of the R.C.R. in officers and men is given in Appendix 1.
Non-permanent:—
- 11 Contingents Canadian Officers' Training Corps. (footnoted: "Form part of the Infantry of the non-permanent Militia with precedence immediately before the G.G.F.G.")
- Governor-General's Foot Guards
- 2 Regiments of 2 battalions.
- 106 Regiments of 1 battalion.
- 2 Independent Companies.
Infantry in the British Army
In the British service the infantry comprises the Brigade of Guards—Grenadier, Coldstream, Scots, Irish and Welsh Guards, known as Household Troops, their duties in peace being connected with the security of the Sovereign—and the Infantry of the Line. Each Regiment, of Guards and of the Line, is composed of 2 or more battalions. (footnoted: "The battalions of the Guards are as follows:—Grenadiers, 3, with a 4th Reserve Bn.; Coldstream, 3, with a 4th Reserve Bn.; Scots, 2, with a 3rd Reserve Bn.; Irish and Welsh, 1 each with a 2nd Reserve Bn.")
Previous to 1882, few of the latter had more than one battalion, when the system of linking individual line regiments in pairs under a Territorial designation came into effect and the old numbers ceased to be employed officially, the expressions "1st (or 2nd) Battalion the Blank and Dash Regiment" being adopted. The same re-arrangement was made with respect to the old County Militia regiments (footnoted: "The Militia trained for 28 days annually in camp or barracks and drew pay; recruits assembled 2 weeks previously for preliminary training.") which became the 3rd (and 4th) battalion of the regiment whose Depôt was established in the county. Similarly the Volunteers (footnoted: "Volunteer units received no pay, but a capitation grant for each "efficient" with extra grants drawn for each officer who passed certain of the examinations set for officers of the Regular Army.") abandoned their old numbers and became the "1st, 2nd, 3rd, etc.) Volunteer Battalion, the Blankshire Regiment," and adopted (in many cases) the uniforms of their respective line battalions, with this difference that silver or white lace and cord took the place of the gold or yellow worn by the Regulars. (footnoted: "Militia officers wore gold and the letter M on the shoulder straps below the badges of rank.")
The Territorial and Reserve Forces Act of 1907 changed the foregoing arrangement. A few Militia battalions were disbanded, and the great majority became the 3rd and 4th "Special Reserve" battalions of those regiments possessing 2 line battalions, or the 4th and 5th of those with 4. The Yeomanry (footnoted: "Cavalry corps originally enlisted from amongst the yeoman or farmer class.") and Volunteers became the Territorial Force, and now appear in the Army List as the 5th (6th, etc.)—Battalion of their line regiment. The use of silver in place of gold on scarlet (or blue) uniforms no longer obtains, the letter T on the shoulder indicating that the wearer belongs to the territorial force. In service-dress, the T is worn below the collar badges.
Canadian Regiments of Infantry and Rifles
 The Canadian Regiments of Infantry and Rifles as classified as being either City or Rural.
The Canadian Regiments of Infantry and Rifles as classified as being either City or Rural.
- City Corps—Corps of the Active Militia (non-permanent) not rural corps. Rural Corps—A Corps of the Active Militia (non-permanent) which performs its annual training in camp.
- The seniority of units is that shewn in the Militia List and is according to their numerical sequence, though in some cases numbers formerly held by regiments, since disbanded, have been given to newly organized units.
The Rifle Regiments are 25 in number, namely,—2nd, 3rd, 8th, 11th, 20th, 22nd, 30th, 38th, 39th, 41st, 43rd, 49th, 51st, 56th, 58th, 63rd, 68th, 76th, 90th, 97th, 103rd. These are in most cases designated further with some territorial or personal reference, such as "Queen's Own Rifles," "Soo Rifles," "Earl Grey's Own Rifles," etc. Rifle regiments are differentiated from other regiments of foot in that their uniform is dark green and that they march past at the "trail" without fixed bayonets instead of at the "slope."
The remainder are styled variously:—
- Grenadier Guards (1st);
- Chasseurs (4th);
- Highlanders (5th, 48th, 72nd, 78th, 79th, 91st, 94th);
- Fusiliers (7th, 11th, 21st, 62nd, 66th, 88th, 101st, 104th, 105th);
- Voltigeurs (9th);
- Grenadiers (10th,100th);
- Rangers (12th, 57th, 74th, 99th, 102nd);
- Light Infantry (15th, 26th, 29th (Highland), 67th, 82nd, 106th);
- Pioneers (23rd);
- Borderers (27th);
- Franc Tireurs (18th);
- Foresters (35th);
- Carabiniers (54th, 65th).
Others have a territorial designation in addition to a number, while some use the number only. A few are authorized to be termed "Royal."
The existing establishments of the infantry and rifle regiments are in a condition of change, some having been authorized to organize on the new 4 (double) company system. On the 8 company system, City corps have 47 privates, and Rural corps 30, except the 29th, 45th, 69th, 73rd, 76th, 82nd, 85th, 89th, 94th, 99th and 108th, which have 47. the 10th and 48th Regiments have 88 privates per company. One is on a 6, and a few on a 4 company basis.
The 2nd and 5th Regiments possess 2 battalions and have a special establishment.

Establishment of the R.C.R.
- Officers – 30
- Other ranks – 296
- Total effective strength – 326
(Not including supernumeraries such as Instructional cadres, Physical Training Instructors, and others not doing duty with the unit.)

Appendix II—Infantry and Rifles
Peace establishments of regiments of the non-permanent Militia on the 8 company basis. Previous to the adoption by certain units of the 4 (double) company system—under authority from M.H.Q.—two establishments obtained, a higher for City Corps, and for the following Rural Corps, 29th, 45th, 69th, 73rd, 76th, 82nd, 85th, 89th, 94th, 99th and 108th and a lower for the remainder of the Rural Corps. Changes are occurring from time to time but what follows indicates the composition of each as taken from Canadian Establishments and amendments to the same, which book must be consulted for exceptions.
| Headquarters | Higher Estb. | Lower Estb. | Remarks |
| Lieutenant-Colonel | 1 | 1 | |
| Majors | 2 | 2 | Only 1 if a 4 C. Regt. |
| Adjutant | 1 | 1 | |
| Musketry Instructor | 1 | 1 | |
| Signalling Officer | 1 | 1 | |
| Quarter-Master | 1 | 1 | Honorary rank. |
| Paymaster | 1 | 1 | Only City Corps, and only Rural Corps whose Paymasters were appointed prior to G.O. 172 of 1910. |
| Medical Officer | 1 | 1 | Now being attached from the A.M.C. |
| Chaplain | 1 | 1 | |
| Sergeant-Major | 1 | 1 | May be a Warrant Officer. |
| Bandmaster or Band Sergeant | 1 | 1 | May be a Warrant Officer. |
| Quarter-Master Sergeant | 1 | 1 | |
| Orderly-room Sergeant | 1 | 1 | |
| Pay Sergeant | 1 | 1 | |
| Included in Headquarters | 1 | 1 | |
| Stretcher-bearer Sergeant | 1 | 1 | |
| Privates, stretcher-bearers | 8 | | |
| Sergeant Cook | 1 | 1 | Not authorized for a regiment of less than 6 companies. |
| Sergeant Drummer | 1 | 1 | |
| Signalling Sergeant | 1 | 1 | |
| Signalling Corporal | 1 | 1 | |
| Privates, signallers | 8 | 8 | |
| Pioneer Sergeant | 1 | 1 | |
| Machine gun N.C.O.'s | 2 | 2 | If corps is in possession of machine guns. |
| Privates, M.G. detachment | 6 | 6 | |
| Bandsmen | 24 | 24 | G.G.F.G. has 32. |
| Batmen | 7 | 7 | |
| Total all ranks included in H.Q. | 76 | 76 | |
| Company Establishment | Higher Estb. | Lower Estb. | Remarks |
| Captain | 1 | 1 | Note:—- 4 Company Regts, 24th, 68th, 84th, 98th.
- 6 Company Regt., 99th.
- 10 Company Regt., 30th.
- 16 Company Regts., 2nd, 5th.
1 Independent Company of Rifles is localized at Grand Forks, B.C., and 1 of Infantry at Nanaimo, B.C. |
| Lieutenants | 2 | 2 |
| Colour Sergeant | 1 | 1 |
| Sergeants | 3 | 3 |
| Corporals | 4 | 4 |
| Bugler | 1 | 1 |
| Private | 47 | 30 |
| | 59 | 42 | |

Posted by regimentalrogue
at 12:01 AM EDT

 After the ceremony has been performed and the couple start to leave, the ushers draw their sabers—or swords for navy—at the command "Draw Sabers" (from one of the ushers) at the foot of the chancel steps and the bride and bridegroom pass beneath the arch. After they have passed through the ushers each take a bridesmaid down the aisle and out of the church. In marching out of the church, the bridegroom, best man and ushers offer their right arms to the bride, maid-of-honor and bridesmaids, thus avoiding entanglement of sabres or swords and dresses, and leaving the left hand free to carry the cap.
After the ceremony has been performed and the couple start to leave, the ushers draw their sabers—or swords for navy—at the command "Draw Sabers" (from one of the ushers) at the foot of the chancel steps and the bride and bridegroom pass beneath the arch. After they have passed through the ushers each take a bridesmaid down the aisle and out of the church. In marching out of the church, the bridegroom, best man and ushers offer their right arms to the bride, maid-of-honor and bridesmaids, thus avoiding entanglement of sabres or swords and dresses, and leaving the left hand free to carry the cap.


 The Canadian Regiments of Infantry and Rifles as classified as being either City or Rural.
The Canadian Regiments of Infantry and Rifles as classified as being either City or Rural.
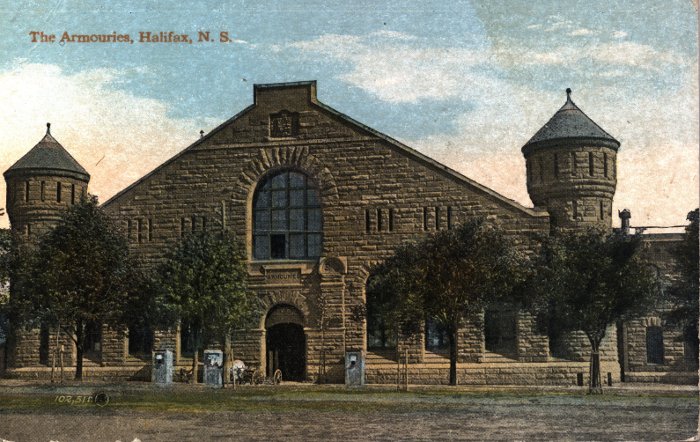






 To-night General Gascoigne inspected the
To-night General Gascoigne inspected the 
 The Montreal Gazette, 18 June 1931
The Montreal Gazette, 18 June 1931






 Ottawa, August 26.—(Special)—Official corroboration has been received of the report that the Canadian Regiment at Halifax is to be relieved from duty by a regiment of the Imperial army. The conformation has come in the form of a cablegram from the quartermaster-general in England to General Parsons, officer commanding the Imperial troops at Halifax, stating that the Fifth Regiment, Royal Garrison Artillery, has been ordered to embark for Halifax about the middle of next month, to replace the Third (Special Service) Battalion, Royal Canadian Regiment. A copy of the cablegram was sent on to Lord Aylmer, the adjutant-general.
Ottawa, August 26.—(Special)—Official corroboration has been received of the report that the Canadian Regiment at Halifax is to be relieved from duty by a regiment of the Imperial army. The conformation has come in the form of a cablegram from the quartermaster-general in England to General Parsons, officer commanding the Imperial troops at Halifax, stating that the Fifth Regiment, Royal Garrison Artillery, has been ordered to embark for Halifax about the middle of next month, to replace the Third (Special Service) Battalion, Royal Canadian Regiment. A copy of the cablegram was sent on to Lord Aylmer, the adjutant-general.



 1. An underestimation, sometimes bordering on the arrogant, of the enemy.
1. An underestimation, sometimes bordering on the arrogant, of the enemy. On 26 June 2016, we shared the story of
On 26 June 2016, we shared the story of 