Topic: CEF
Anyone who researches soldier of the Canadian Expeditionary Force eventually comes across the name of Edward Wigney. A tireless researcher and compiler of information, Edward left behind a series of works that presented an incredible amount of his own research.
 The C.E.F. Roll of Honour (1996)
The C.E.F. Roll of Honour (1996)
The best known book produced by Wigney is "The C.E.F. Roll of Honour." In this 866-page volume, Ted compiled a comprehensive listing of the 67,000 "members and former members of the Canadian Expeditionary Force who died as a result of service in the Great War, 1914-1919." Using the Canadian Books of Remembrance and the War Graves Registers as his starting point, he tackled the great challenges of reconciling conflicting information on individuals, the use of aliases and the many errors of spelling and transcription of numbers that previous recorders left in their paths. Wigney's Roll of Honour is an impressive work linking the soldiers personal details to unit, date or death, cemetery and notes containing details of unit of enlistment, nature of death and age where known.
"The CEF Roll of Honour" is available through MedalsofWar.com.
This book lists every Canadian servicemen who died during WWI. It involves seven years of work and brings together previously disjointed and unknown information into one substantial text. This book is a joy to peruse and easy to use in that all 67,000 names are listed alphabetically! This is a limited quantity printing and will be a necessary addition to any library. 880 pages, beautiful hardcover; 67 000 names; full Christian name, rank, serial number; place of burial; honours and awards, cross-referenced alias names; cause of death (i.e., KIA, DOW); Canadians who died serving with British, Australian, New Zealand, South African and U.S. forces; identification of all North American Indians; P.O.W.'s; listed alphabetically and much more. Probably the most important book you can own on WWI.
 Mentioned in Despatches of the C.E.F. (2000)
Mentioned in Despatches of the C.E.F. (2000)
Researching Mentions in Despatches (MiD) can be a frustrating exercise because the varying ways names might be listed in the London Gazette can make for slow and seemingly futile searches. This can be compounded when a recipient may have received more had one mention, or when a note in a file or personal history identifies the receipt of a Mention in Despatches, but it turns out to be something quite different.
Wigney's "Mentioned in Despatches of the C.E.F." is actually two compiled lists. The first is the listing of those Mentioned in Despatches and Names Brought to Notice to the Secretary of State for War (A List) of the Canadian Expeditionary Force. This list includes the recipient's details, with rank at the time of each award as applicable, unit, and the London Gazette issue number and date of issue.
The second part of this volume provides the listing of those Names Brought to Notice to the Secretary of State for War (B List) of the Canadian Expeditionary Force. Similar to being Mentioned in Despatches, this degree of notice did not include the privilege of wearing the MiD emblem.
Self published by Wigney, copies of Mentioned in Despatches can often be found through on line sources.
 Guests of the Kaiser; Prisoners of War of the CEF 1915-1918 (2008)
Guests of the Kaiser; Prisoners of War of the CEF 1915-1918 (2008)
Sadly, Edward Wigney died on 28 Sep 2008 while completing preparations for publish "Guests of the Kaiser." His family ensured that the manuscript was completed and his roll of 3800 CEF Prisoners of War became an available reference to Canadian Great War researchers.
"Guests of the Kaiser" is available through Norm Christie's CEF Books.
The late Ted Wigney was Canada's foremost Great War researcher. His Roll of Honour of the CEF has become the WWI Researchers Bible. Ten years in the making in Guests of the Kaiser Ted has compiled the details of 3800 CEF POWs. The majority were taken at Ypres and Mount Sorrel, but Ted's meticulous list gives details of all POWs, those lost on Trench Raids, The March Retreats, and even divulges the Alias of the RCR deserter, Otto Doerr, who went over to the Germans before Vimy, and gave up much information on the Canadian Plans. Only Ted Wigney could unravel the story of the RCR deserter. The book also contains the stories of the 100 Escapers, gallantry awards, and many other fascinating details of this forgotten piece of Canadian history.


 Over 350,000 Canadians received the
Over 350,000 Canadians received the 

 While I do not know where the Canadian Forces currently stands on the possibility of Battle Honours being awarded for
While I do not know where the Canadian Forces currently stands on the possibility of Battle Honours being awarded for 


 The Royal Canadian Regiment
The Royal Canadian Regiment Anyone who has followed the news reporting around
Anyone who has followed the news reporting around 
 Sacred Places; Canadian Cemeteries of the Great War
Sacred Places; Canadian Cemeteries of the Great War Remembered; The History of the Commonwealth War Graves Commission
Remembered; The History of the Commonwealth War Graves Commission
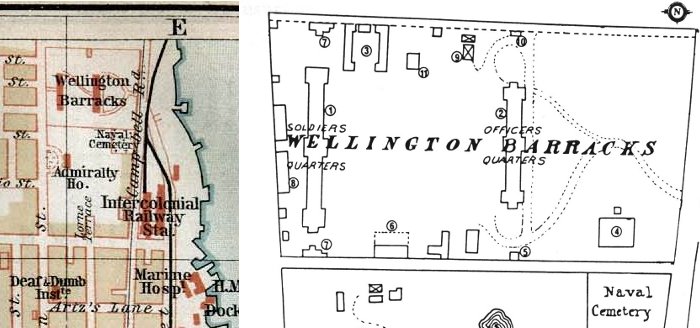



 Militia General Orders
Militia General Orders It was during the first Fenian raids in 1866, that the only Victoria Cross to be awarded for actions in Canada was granted. This award, for an act of gallantry not in the presence of the enemy (which was allowed by the terms and conditions for the VC for a brief period) was earned by
It was during the first Fenian raids in 1866, that the only Victoria Cross to be awarded for actions in Canada was granted. This award, for an act of gallantry not in the presence of the enemy (which was allowed by the terms and conditions for the VC for a brief period) was earned by  From the excellent British service medals reference "
From the excellent British service medals reference " 13. Desertion, Fraudulent Enlistment, and absence without leave.—A distinction is made by the [Army] Act between desertion and fraudulent enlistment. The latter, which is constituted a separate offence bu s. 13 is dealt with hereafter.
13. Desertion, Fraudulent Enlistment, and absence without leave.—A distinction is made by the [Army] Act between desertion and fraudulent enlistment. The latter, which is constituted a separate offence bu s. 13 is dealt with hereafter.
 Connecting File, January, 1946
Connecting File, January, 1946



 For those interested in Canadian miliary dress, and headdress, over the ages, a new book on Canadian military headdresss is available that would be a welcome addition to the reference shelf of any collector, curator, or historian. “Fuss & Fashion” by Clive Law is available from Service Publications.
For those interested in Canadian miliary dress, and headdress, over the ages, a new book on Canadian military headdresss is available that would be a welcome addition to the reference shelf of any collector, curator, or historian. “Fuss & Fashion” by Clive Law is available from Service Publications.

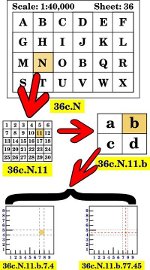






 The following Imperial Regulations apply in all cases where medals have been granted to miltiamen in Canada:—
The following Imperial Regulations apply in all cases where medals have been granted to miltiamen in Canada:— Special Provisions for the Victoria Cross
Special Provisions for the Victoria Cross
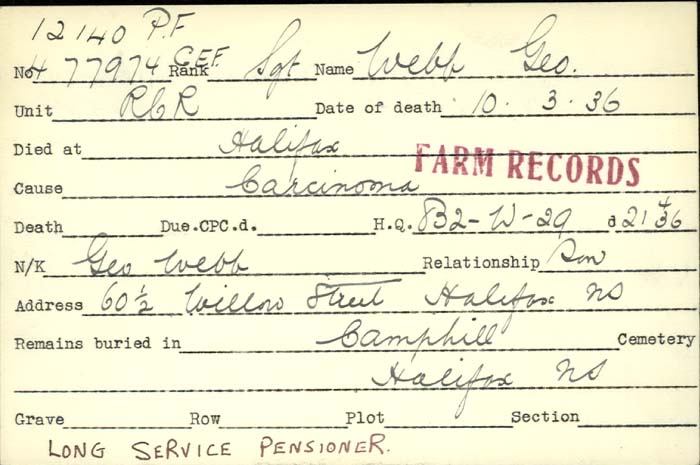 Above is shown the Veteran's Death Card of
Above is shown the Veteran's Death Card of